Tutorial
In this page, we offer an example analysis of the DEBIAS-M classifier. For this analysis, we use the collection of HIV studies that is available on Synapse. For a full set of analyses performed by DEBIAS-M on this dataset, please refer to the DEBIAS-M manuscript.
Loading packages, data
## import packages
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from debiasm import DebiasMClassifier
from debiasm.torch_functions import rescale
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc
from sklearn.metrics import pairwise_distances
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from skbio.stats.ordination import pcoa
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import glob
import os
def load_HIVRC(data_path):
df = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(data_path,
'insight.merged_otus.txt'),
sep='\t',
index_col=0
).iloc[:, :-1].T
## we generally recommend some minimum presence OTU filter
df = df.loc[:,((df>0).sum(axis=0) > df.shape[0]*.05 )]
md = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(data_path,
'metadata.tsv'),
sep='\t')
md = md.set_index('SeqID').loc[df.index]
md['label'] = md['hivstatus']==1
return((df, md))
df, md = load_HIVRC(data_path='.') ## this assumes the data is downloaded to the same directory, can change as needed
X_with_batch = pd.concat([pd.Series(pd.Categorical(md.Study).codes,
index=md.index,
name='batch'),
df
], axis=1)
PCoA of raw data
# Compute a distance matrix (using Bray-Curtis distance)
distance_matrix = pairwise_distances(rescale(df.values),
metric='braycurtis')
# Perform PCoA analysis
ordination_result = pcoa(distance_matrix, number_of_dimensions=2)
# Extract the first two principal coordinates
x_coords = ordination_result.samples.iloc[:, 0]
y_coords = ordination_result.samples.iloc[:, 1]
plt.figure(figsize=(8,8))
sns.scatterplot(x=x_coords,
y=y_coords,
hue=md.Study.values,
s=100
)
# Add labels and title
plt.xlabel('PCoA 1')
plt.ylabel('PCoA 2')
plt.title('PCoA of the raw data')
plt.legend().remove()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()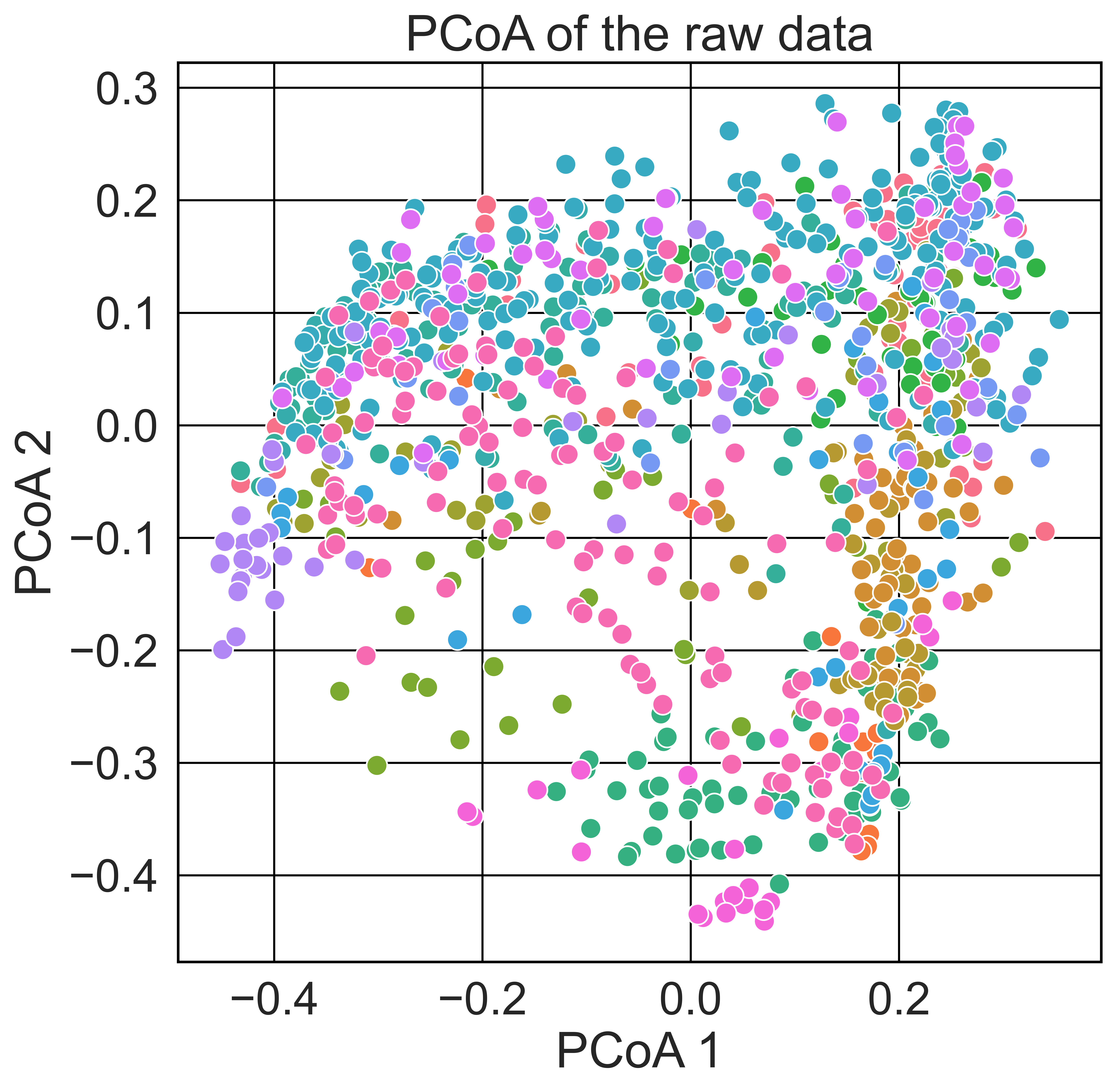
Predictive analysis
We demonstrate the following code using DEBIAS-M with default parameters, using one study as a test set.
test_sd_number=5 ## index of the test study
train_inds = md.Study!=md.Study.unique()[test_sd_number]
## run DEBIAS-M
dmc=DebiasMClassifier(x_val=X_with_batch.loc[~train_inds].values) ## provide the read counts for the test set
dmc.fit(X_with_batch.loc[train_inds].values, md.label.loc[train_inds].values) ## the read counts and labels for the training studies
## transform the data
x_dmc=dmc.transform(X_with_batch)
# Generate a PCoA plot
## Compute a distance matrix (using Bray-Curtis distance)
distance_matrix = pairwise_distances(x_dmc.values,
metric='braycurtis')
# Perform PCoA analysis
ordination_result = pcoa(distance_matrix, number_of_dimensions=2)
# Extract the first two principal coordinates
x_coords = ordination_result.samples.iloc[:, 0]
y_coords = ordination_result.samples.iloc[:, 1]
plt.figure(figsize=(8,8))
sns.scatterplot(x=x_coords,
y=y_coords,
hue=md.Study.values,
s=100
)
# Add labels and title
plt.xlabel('PCoA 1')
plt.ylabel('PCoA 2')
plt.title('PCoA plot of the DEBIAS-ed data')
plt.legend().remove()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()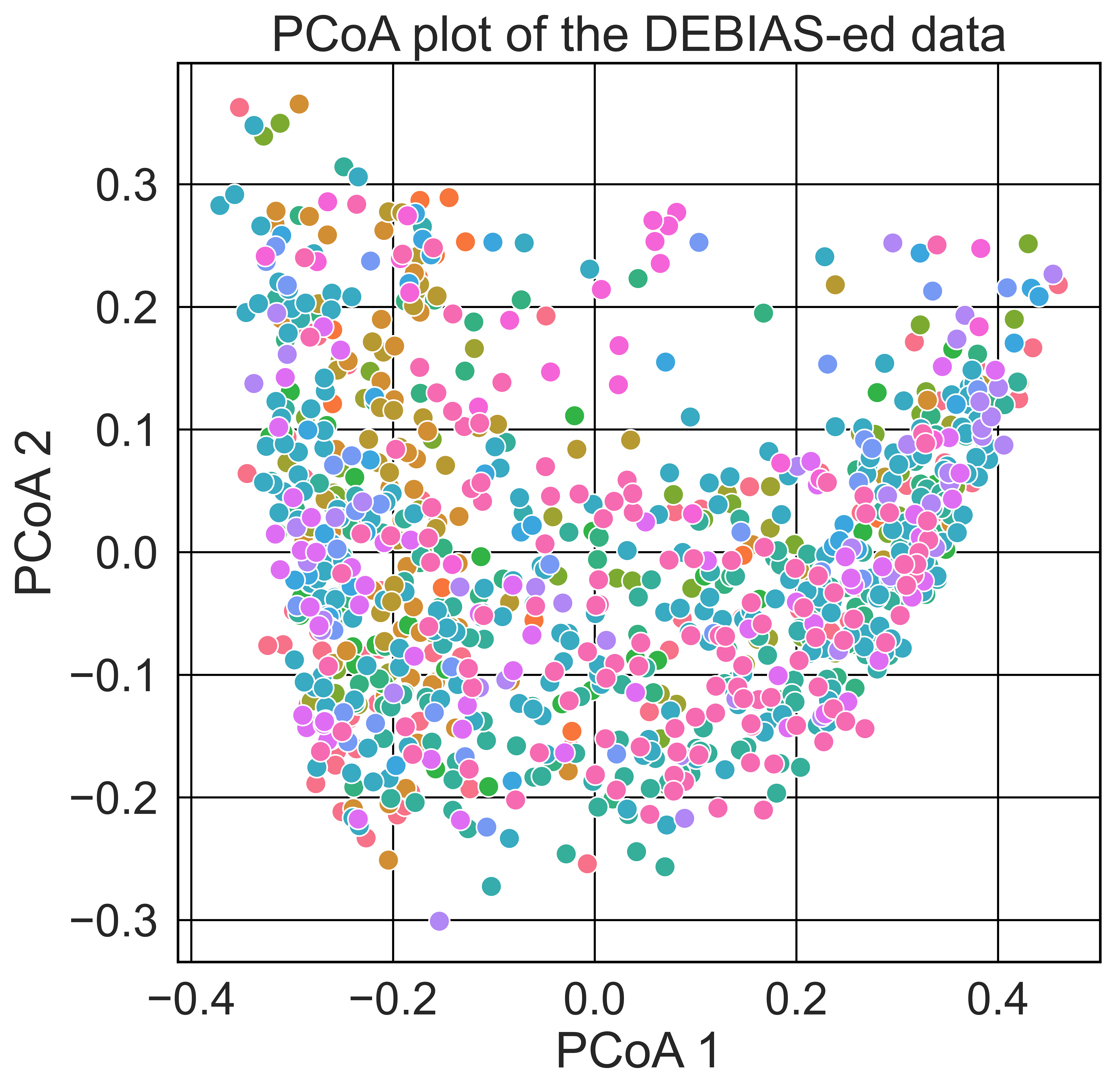
Assess predictions
# Function to plot ROC curves for multiple prediction arrays
def plot_roc_curves(predictions_list,
y_true,
name_list):
plt.figure(figsize=(8,8))
for i, y_pred in enumerate(predictions_list):
fpr, tpr, _ = roc_curve(y_true, y_pred)
roc_auc = auc(fpr, tpr)
plt.plot(fpr, tpr, label=f'{name_list[i]} (AUROC = {roc_auc:.2f})', linewidth=5)
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], 'k--', lw=5)
plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')
plt.ylabel('T"rue Positive Rate')
plt.title('ROC Curve')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.grid(False)
plt.title('ROC curve of DEBIAS-M cross-study HIV predictions')
## run baseline linear model on raw data (equivalent to debias-m's model without the bias inference)
lr=LogisticRegression(penalty='none',
max_iter=int(1e3),
solver='newton-cg'
)
lr.fit(rescale(df.loc[train_inds]), md.label.loc[train_inds])
plot_roc_curves([lr.predict_proba(df.loc[~train_inds])[:, 1],
dmc.predict_proba(X_with_batch.loc[~train_inds].values)[:, 1] ],
md.label.values[~train_inds.values],
['Raw',
'DEBIAS-M'
])
plt.show()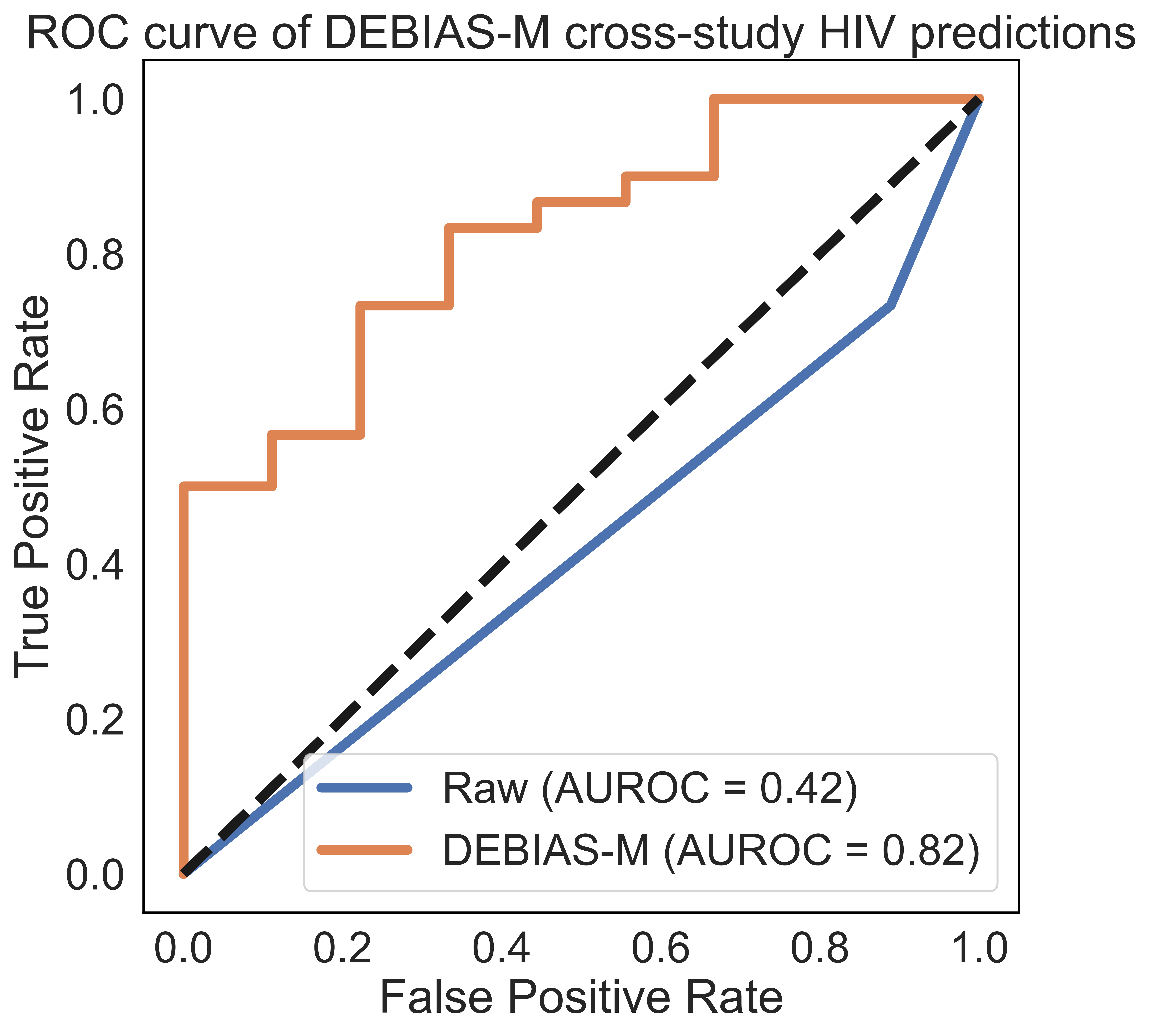
See also:
Multitask DEBIAS-M
Classifier
The multitask DEBIAS-M classifier
DebiasMRegressor
Implementation of a DEBIAS-M regressor
For more
background on DEBIAS-M, refer to our
manuscript.